While irregular verbs can be very frustrating to conjugate, they are still used in sentences the same way as other verbs are. As with all other verbs, irregular verbs must follow subject-verb-agreement and match the subject of the sentence or clause they are used in. Like regular verbs, irregular verbs can be action verbs, stative verbs, or linking verbs. Just like regular verbs, irregular verbs can also be used as either transitive or intransitive verbs.
Main verbs also called lexical verbs are those verbs that can stand alone without the help of another verb to complete a sentence. A main verb expresses the action or state of being of the subject. When expressing an action, a main verb is an action verb. When it expresses the subject's state of being, it takes a different name of linking verb. Every sentence must have a main verb, without which a sentence is incomplete and thus, meaningless. Most verbs are main verbs and any verb in a sentence that is not an auxiliary verb is a main verb .The main verb can be in the present or past tense forms.
In these constructions, the "to be" verb will follow the standard rules for subject verb agreement. The examples below have sentences using "to be" verbs in different tenses. Before we explore irregular verbs, it is important to briefly explain regular verbs. Regular verbs follow the general rules of verbs when we use them in the simple past tense or turn them into a past participle of the verb. In both cases, we typically add -ed, -d, or, sometimes, a -t to the root form of the verb to make the simple past tense or to create a past participle. For example, both the simple past tense and past participle of climb is climbed.
The past participle is used in the present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect verb tenses and follows the words has, have, had, and will have. "To be" verbs change almost more than any other verb. Let's learn how to use "to be" verbs correctly. Refer back to this lesson when you have questions about how to use them in the future. It can be hard to recognize that a verb is in fact an irregular verb when using the simple present tense. However, things become easier when we see or hear sentences that use the simple past tense or verb tenses that use the past participle.
Because they love to break the rules, irregular verbs are usually easy to spot when they are used in the simple past tense or as past participles in sentences. For example, see if you can spot which of the verbs used in the following three sentences is an irregular verb. When giving imperatives or commands, "to be" verbs stay in the base form of be and typically stay at the beginning of the sentence. In these sentences, the subject is implied so it doesn't have to be written, that is why you only see the "to be" verb followed by the complement. The future tense is one of the easiest tenses to learn because it has no irregular forms.
Just as its name suggests, it's used to describe actions that will happen in the future. It is formed by combining the helping verb will with the base form of the main verb. Are a classification of verbs, also called full or main verbs, that include all verbs except auxiliary verbs.
In other words, a lexical verb can be any verb, which is not an auxiliary verb. It is used as the main verb in the sentence to show an action or a state of being of the subject. A verb phrase in a sentence begins with a lexical verb. The correct "to be" verb to use depends on your subject and tense. This chart shows you proper subject verb agreement with "to be" verbs. Don't stress over irregular verbs and their use!
Let Thesaurus.com's Grammar Coach™ do the hard work. This writing tool catches grammar and spelling errors and provides Thesaurus-powered synonym suggestions. Using machine learning, Grammar Coach™ can spot the difference between the different verb tenses, their correct and incorrect uses—and much more!
Whether you're writing in the past, present, or future, perfect grammar has never been easier. Well … this is where things get complicated. For example, the simple past tense of the irregular verb run is ran, and the simple past tense of the irregular verb take is took. The past participles of irregular verbs don't follow the rules either.
For example, the past participle of run is … run, and the past participle of take is taken. In the Indo-European languages, verbal adjectives are generally called participles. English has an active participle, also called a present participle; and a passive participle, also called a past participle. The active participle of break is breaking, and the passive participle is broken.
Other languages have attributive verb forms with tense and aspect. This is especially common among verb-final languages, where attributive verb phrases act as relative clauses. The verb in a sentence expresses action or being. There is a main verb and sometimes one or more helping verbs.
("She can sing." Sing is the main verb; can is the helping verb.) A verb must agree with its subject in number . Verbs also take different forms to express tense. Main verbs can be transitive verbs which have direct objects, or intransitive verbs which take no direct object.
The main verb changes in form to agree with the subject in number , person and tense. For the most part, many irregular verbs do follow the rules when used in the simple present tense. For example, the following sentences all use irregular verbs in the simple present tense.
You will notice that none of these verbs are breaking the typical rules of verbs. Intransitive and transitive verbs are the most common, but the impersonal and objective verbs are somewhat different from the norm. As a rule, my sons aren't thrilled to talk about grammar with me. Comments like "Wait—is this a linguistics thing?" and "Mom, Dad's talking grammar again!" have found their way into the conversation at times. But one day I happened to be thinking, out loud, about auxiliary verbs.
Depending on the language, verbs may express grammatical tense, aspect, or modality. Grammatical tense is the use of auxiliary verbs or inflections to convey whether the action or state is before, simultaneous with, or after some reference point. They do not learn the present participle and 3rd person singular present simple for regular or irregular verbs for another very simple reason - they never change. In this lesson we look at the forms of main verbs and helping verbs followed by a quiz to check your understanding.
An independent clause needs a complete verb. Verb forms such as the -ing form and the past participle are not complete because they do not show tense. They need auxiliary verbs to complete their meaning as a verb of a clause. A complete verb includes a verb form preceded by any necessary auxiliary verb or modal auxiliary verb. The linking "to be" verb describes the condition of the subject.
Below are a few sentence structures using the linking "to be" verbs. The previous section contained examples of what most beginners need to learn for using "to be" verbs correctly. In this section, we'll be covering many other ways to use them. All languages can express modality with adverbs, but some also use verbal forms as in the given examples. If the verbal expression of modality involves the use of an auxiliary verb, that auxiliary is called a modal verb.
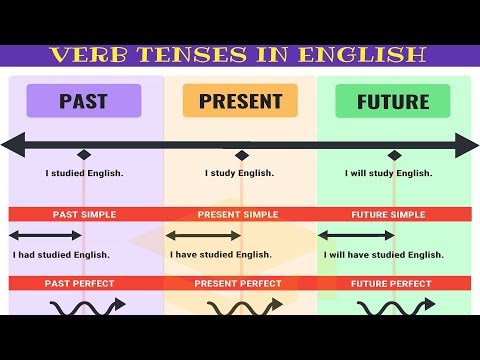
This lesson will help you understand and review all of the different verb tenses in English. You will review how to form each tense using regular and irregular verbs. This lesson also focuses on WHEN to use each of the verb tenses and the differences in meaning between them.
On the other hand, pronouns are a good example of a closed class. Look at all the failed attempts through the centuries to add a gender-neutral third-person singular pronoun to the language. You can make irregular verbs easier for yourself in the future by just learning them right from the beginning.
Every time you learn a new verb, learn its tenses as well. The list of irregular verbs is not a very long one, when you consider that there are over a million words in the English language! It can still be tough to learn them, if you don't know where to start. Listed below are some more irregular verbs you are likely to see very often.
The root form of the verb is followed by first the simple past tense and then the past participle. Irregular verbs are one of the trickiest types of verbs—and words—to use. For the most part, there is no general rule or pattern that helps you figure out how to conjugate an irregular verb.
what are eight forms of be verbs
You will simply need to learn how to conjugate each irregular verb as you find them—thanks a lot, English! Fortunately, our incredible dictionary will help you discover which verbs are irregular verbs and what each of their forms looks like. Knowledge of grammar rules and the six verb tenses is key to writers being able to identify errors and use tense consistently; verb tense refers to the time that action occurs. Explore the correct usage of present, past, future, present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect tenses. Perfect tenses show when an action happened in relation to another action.
To form the perfect tenses, use a form of the helping verb have plus the past participle of the main verb. Despite sometimes needing "be" verbs, strong writers reword sentences to utilize more active, powerful verbs and reduce wordiness. We use modal helping verbs to change the "mood" of the main verb. As you see, modal verbs have only one form each. The tables on this page show the forms of all helping verbs.
Not all irregular verbs are commonly used. You might never use a word like broadcast, and you'll probably only see the word abide as part of the phrase law-abiding citizen (that's someone who follows the law). Irregular verbs don't follow any rules, which is what makes them so hard to remember. But some irregular verbs follow a similar pattern.
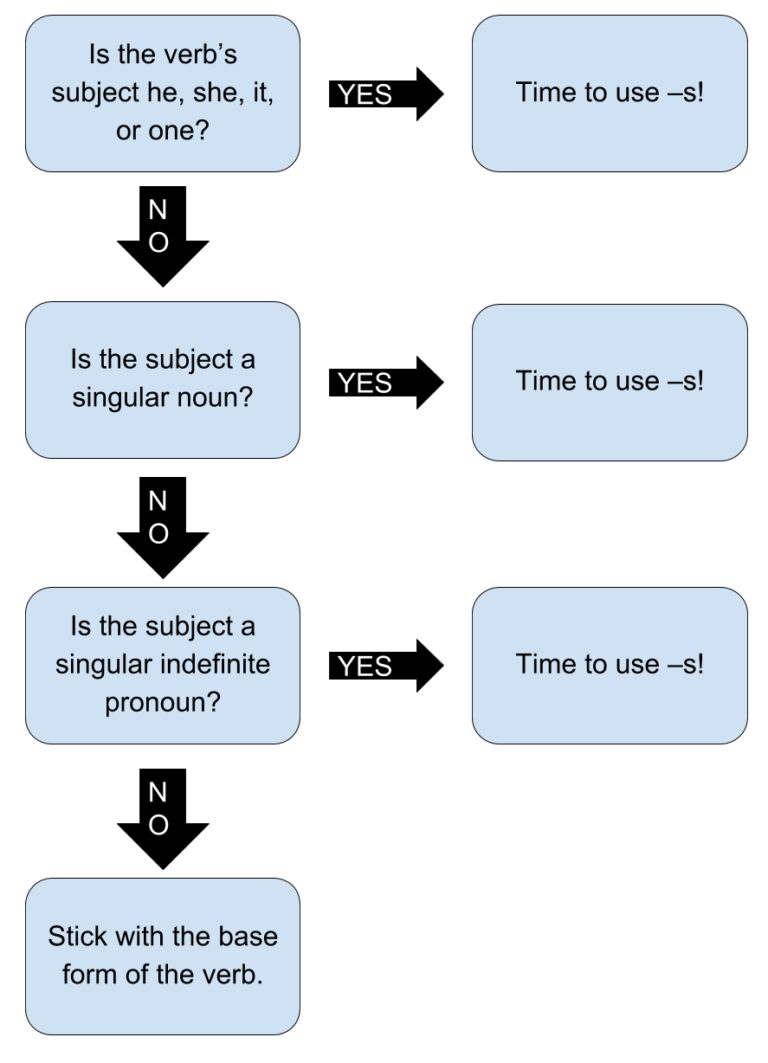
Instead of learning the verbs in alphabetical order, try putting them in similar groups. In languages where the verb is inflected, it often agrees with its primary argument in person, number or gender. With the exception of the verb to be, English shows distinctive agreements only in the third person singular, present tense form of verbs, which are marked by adding "-s" or "-es" . The rest of the persons are not distinguished in the verb (I walk, you walk, they walk, etc.). The root form of a verb is used to create other forms of the verb when conjugated.
This is always true with regular verbs, but may not apply with irregular verbs, depending on the tense. The examples below illustrate this concept. A subject-verb agreement is when the object in a sentence connects to the motion in a sentence in numerical value, meaning they are either both singular or both plural. Learn more about identifying subject-verb agreements, simple and compound sentence, subject-verb inversion, and indefinite pronouns to avoid errors.
Subject-verb agreement is when plural verbs are used with plural nouns and pronouns, and singular verbs are used with singular nouns and pronouns. Learn about uncommon group and singular nouns, indefinite pronouns, and how to use proper subject-verb agreement for grammatically correct writing. The present progressive tense is typically used to talk about something that is happening right now. It can also be used to talk about a future action or an action that is occurring at the same time as another one. It is formed by using a present tense form of the verb to be plus the present participle of the main verb.
A noun is a word for a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are often used with an article , but not always. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter; common nouns do not.
Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract. Nouns can function in different roles within a sentence; for example, a noun can be a subject, direct object, indirect object, subject complement, or object of a preposition. Shouldmustought tosemi-modal verbsneeddareused to We use the word "form" to mean the "shape" or "writing" of the actual verb itself.
We use the different verb forms to make the tenses and other verb structures, but they are not the same thing. Main verbs are used with the auxiliary verbs in questions, negative statements, tenses, and passive sentences. The "to be" verb used in the question tag must be the same one used in the statement. These are examples of how you will see "to be" verbs most often.